What Are ESG Goals? Meaning, Components, Examples & Reporting

What ESG Goals Are and Why They Matter
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals refer to business objectives strategised by an enterprise to identify, manage, and monitor sustainability-related risks and opportunities. They aim to measure the impact of a business on the environment, communities, and executive stakeholders. Not only do positive ESG goals help businesses identify risks and contribute to the world at large, but they also boost the brand’s image.
In a world where rising carbon emissions and sustainability are pressing concerns, ESG goals for companies help manage environmental, social, and governance impact while driving stakeholder engagement and brand value. Naturally, they form an important part of the core business strategy among thriving businesses.
Understand The Core Components Of ESG Goals
ESG goals for companies are comprised of three core components:
Environmental
The first dimension of ESG goals, the environmental component, is used to determine how a business and its activities impact our natural environment. The focus is on aspects such as:
- Carbon footprint
- Management of waste
- Pollution mitigation
- Conservation of non-renewable resources
- Protection of biodiversity and naturally occurring ecosystems
Social
The social dimension of ESG goals takes into account the human factor and impact on individuals and communities made by virtue of a business’s regular operations. Parameters for measuring include:
- Labour rights and safety
- Healthy workplace culture
- Diversity, equity, and inclusivity in the workplace
- Community engagement
- Customer of data privacy and protection
Governance
The governance dimension of ESG goals focuses on internal dynamics and the responsible functioning of a business. Standards in focus include:
- Structure and diversity of a board
- Integrity and accountability among decision-makers
- Executive compensation
- Risk management, regulatory compliance, and protection of shareholder rights
- Other ethical business practices
How To Define Effective Company ESG Goals
Setting impactful company ESG goals enables your business to turn big picture sustainability targets into organically achievable objectives. Here’s how you can define the effective ESG goals for your business:
1. Conduct Standard Assessments
Being transparent and publicly disclosing your targets has a positive impact on the credibility of your business.
2. Decide on SMART Goals
Setting ESG targets that are not just aspirational but can be achieved through realistic and organic progress within a specific time period facilitates the overall long-term scalability of your business.
3. Align Goals With Global Standards
When your ESG goals for companies are aligned with global ESG standards, your business gains a competitive advantage. Aligning with frameworks like GRI (Global Reporting Initiative) and UN Sustainable Development Goals enhances its attractiveness for investors.
4. Practise Transparency & Disclosure
Transparent and consistent disclosure of targets strengthens organisational credibility. Sharing this information with all stakeholders uplifts your brand image and positions your business as reliable and trustworthy.
5. Review & Grow
Monitoring your growth in alignment with the set ESG goals by reviewing reports enables your business to tackle challenges effectively. Consistent tracking of KPIs facilitates improved decision-making in the future.
Examples Of Strong ESG Goals In Business
Several companies have set off a ripple effect on sustainability trends among businesses through the positive ESG initiatives they have adopted. Here are a few examples of ESG goals practising companies:
Mattel
A renowned toy company across the globe, Mattel has adopted two key programs in order to commit to sustainability and positive social impact - “Sustainability 360” and “Corporate Responsibility Strategy.”
Costco
One of the biggest retail giants in the United States, Costco, has undertaken several ESG initiatives to strengthen its commitment to sustainability and ethical ESG practices. The Annual Sustainability Report 2025 of the retailer outlines some of them:
- Fuel transition plans
- Responsible sourcing methods
- Animal welfare
- Water conservation
- Reduced workplace inequalities
Microsoft
Becoming carbon negative by 2030 is one of the central examples of ESG goals Microsoft has committed to. The company’s “Environmental Sustainability Vision” program’s report for 2025 outlines progress in improving water replenishment and usage efficiency.
Steps To Align ESG Goals With Corporate Strategy
A step-by-step process that incorporates ESG goals with broader business objectives can support long-term financial resilience and investor confidence.
- Step 1: Set strategic ESG priorities.
- Step 2: Integrate ESG into the business mission.
- Step 3: Set SMART targets and make them known.
- Step 4: Conduct periodic reviews.
Challenges In Setting and Achieving ESG Goals
Addressing challenges faced by companies worldwide can aid in achieving ESG goals more efficiently. Some of the top challenges faced by businesses are:
1. Absence of a Single Standard
Currently, businesses have to navigate among frameworks like GRI (Global Reporting Initiative), ISSB (International Sustainability Standards Board), SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board) and many more.
Building flexibility in such an environment is key to efficient compliance with standards.
2. Greenwashing
An unethical practise and a risky business tactic, damage to reputation is just one Google search away when businesses engage in greenwashing.
ESG reporting through transparent data insights and accurate reporting ensures the long-term health of businesses and reduces legal risks.
3. Conflict of Interest
Tackling financial goals while prioritising sustainability is something businesses continue to attempt to balance.
Building trust with all stakeholders, on every level of an organisation's functioning, can help achieve ESG targets along with a balance in decision-making.
Measuring and Reporting Progress Against ESG Goals
Monitoring your ESG performance metrics is key when quantifying the impact of your ESG goals and making future-focused decisions. Common ESG metrics include:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Generation of Waste
- Impact on Biodiversity
- Labour Practices
- Product Safety and Quality
- Executive Compensation
- Anti-Corruption Regulations
ESG Goals: Key Takeaways
Value judgment is central to investment decisions for investors and customers alike.
- ESG goals shape the long-term brand reputation of your business.
- They aid in mitigating risks and position a brand positively.
- SMART goals help balance short-term financial goals with sustainability targets.
- Consistent monitoring of ESG metrics aids in refining strategies.
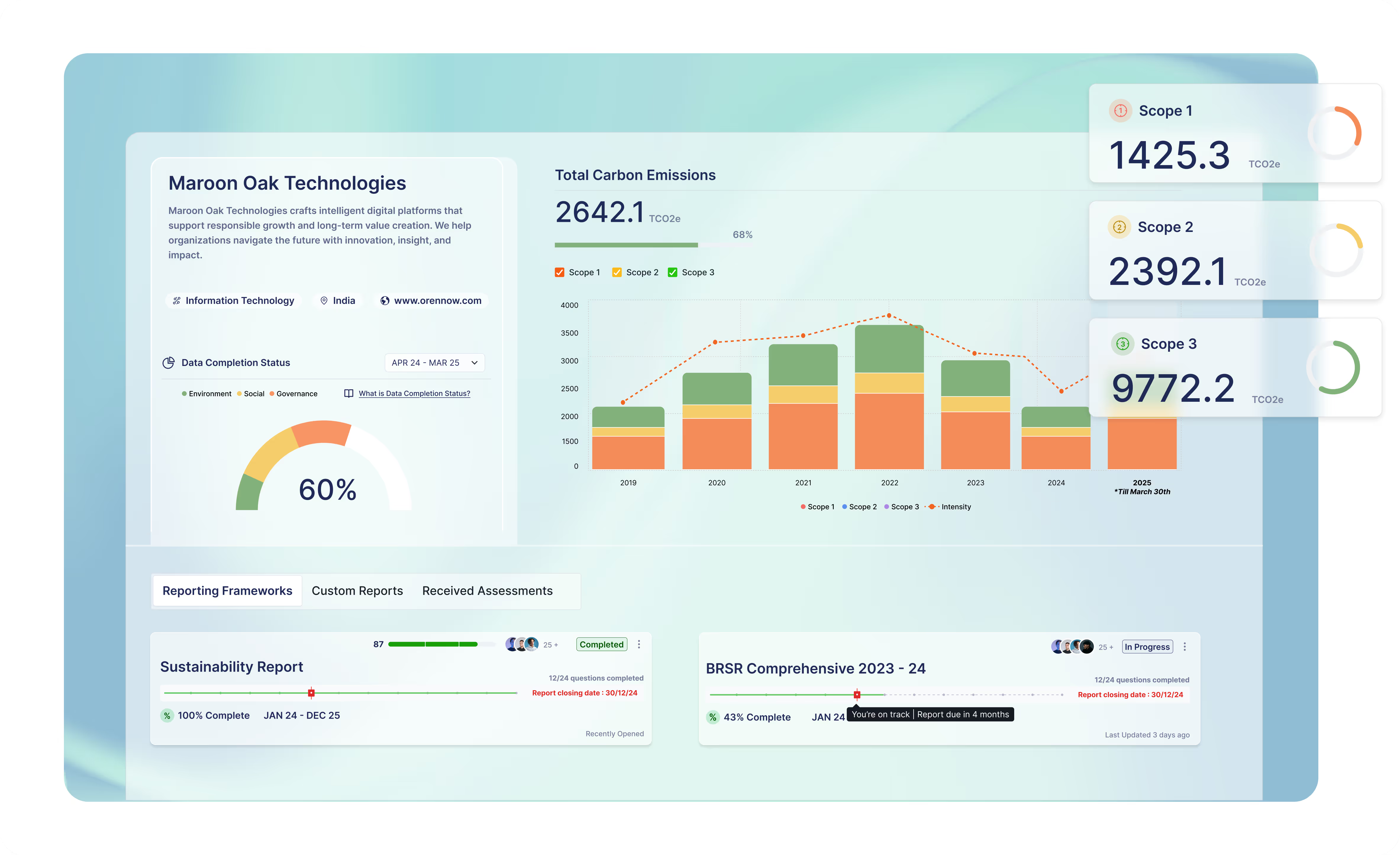
When optimising ESG goals, the maturity assessment tool of Oren enables you to receive a comprehensive sustainability report of your business. Accurate data collection and compliance are accompanied by insightful analyses to aid you in better aligning ESG with corporate goals. Enhance carbon accounting and make informed supply chain decisions with ease!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are ESG goals?
ESG goals are objectives organisations set to manage environmental, social, and governance risks and opportunities.
Q2. Why are ESG goals important?
ESG goals help businesses manage potential risk and present them positively for investors and consumers alike. They are crucial in complying with global regulations and achieving long-term gains.
Q3. How do companies set effective ESG goals?
Enterprises are able to decide on effective ESG goals through a primary material assessment of where a business stands currently concerning ESG standards. It helps align company ESG goals with the overall business strategy. Consistent monitoring and timed reports help review performance metrics and refine goals.
Q4. What is the difference between environmental, social, and governance goals?
Environmental goals include standards that have to do with our natural environment. For example, greenhouse gas emissions, waste management, and water usage. Social goals in company ESG goals indicate aspects like labour practices, fair pay, diversity, and equity. Lastly, governance standards include the anti-corruption regulations and executive compensation of the business.
Q5. How are ESG goals measured?
ESG goals for companies are measured by tracking and quantifying metrics like the carbon footprint of a business, how much energy and water it uses, and the amount of waste it produces. The social impact of the products manufactured and the working conditions of employees are also factored in.
Q6. Can ESG goals improve company performance?
ESG goals can significantly contribute to improving company performance in the long-term by drawing in investors and loyal customers.
Q7. What common mistakes should be avoided when setting ESG goals?
ESG goals should be considered an integral part of your business plan. False claims should be absolutely avoided, and reviews should be accurate.